| Román Fernández Vila
| 2020 | Material Gesture: Stone | ETH Zürich
| Professor: Anne Holtrop | Assistants: Stephan Lando + Yukio Shigeta + Cecilia Marzullo
Place, matter, gesture. Introduction
The research that has been developed explores the dialogue that can exist between positive and negative surfaces, between void and matter, and regarding stone topic, between the material quarried and its quarrying site. As we all know, stone comes from quarries, it has to be extracted from earth. This essential action is therefore creating both void and pieces of material in one gesture. In a specific situation where stone can be excavated from the building site, so the extraction and construction site coincide, this main characteristic of stone as a building resource becomes a powerful tool of design. ¿How can we develop a way of making that preserves the tension between the stone quarried and the void left, and an architecture that grows up from in between this phenomenon?
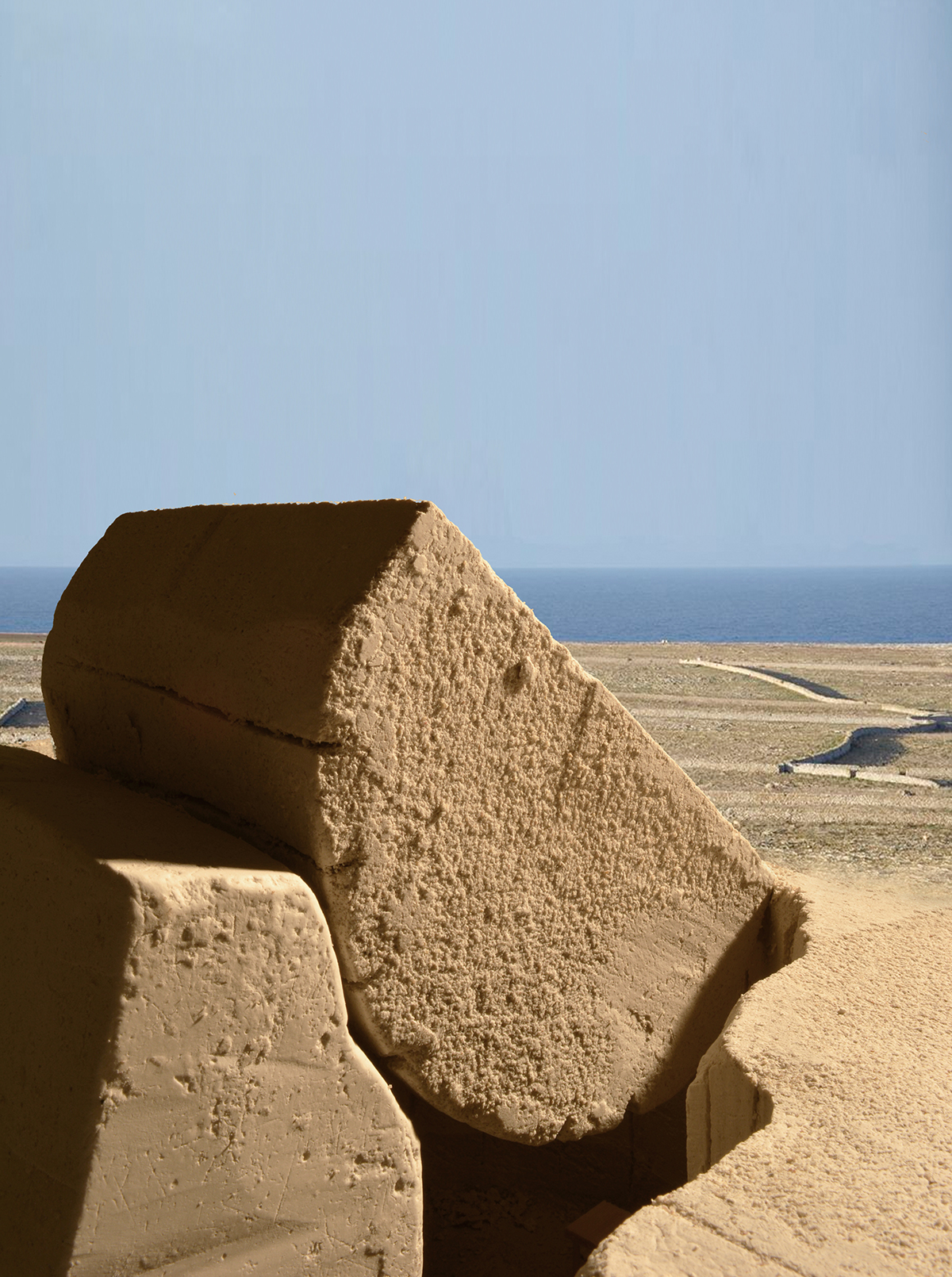
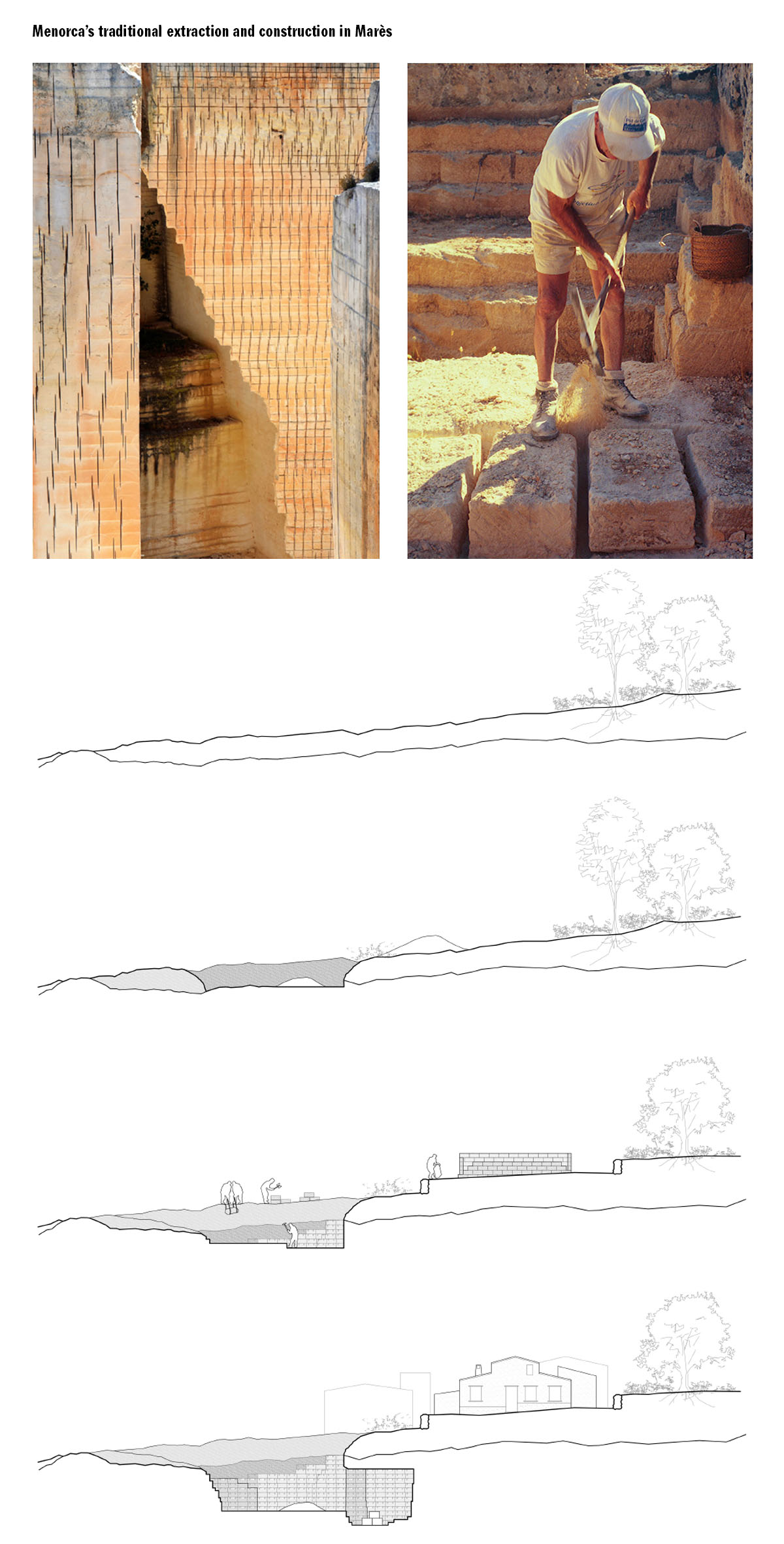
The chosen stone is Marès sandstone from Menorca, a Spanish island in the Mediterranean Sea. In Menorca the recollection of rocks to build dry stone walls and the opening of little quarries directly on rural building sites is a crucial part of vernacular’s construction history, and so the topic engages directly with the site through its historic material ways of making.
With the aim of truly connecting and embracing with Menorca’s quarrying and building tradition, the research started searching for the essential characteristics of its practice. Below the specific sizes or forms of stone blocks in the island, we identify a direct and tense relation between the activities of quarrying and building hold by the fact that extraction sizes are kept. This creates a language of traces and proportions that connects the excavation in the quarries and the resultant architecture. In order to point out this material gesture in Menorca’s constructive tradition, a new extraction technique is introduced on the island, with its autonomous traces, shapes and sizes, but implemented as a process of excavation and building where quarrying characteristics are kept, giving continuity to the island’s constructive tradition explored.
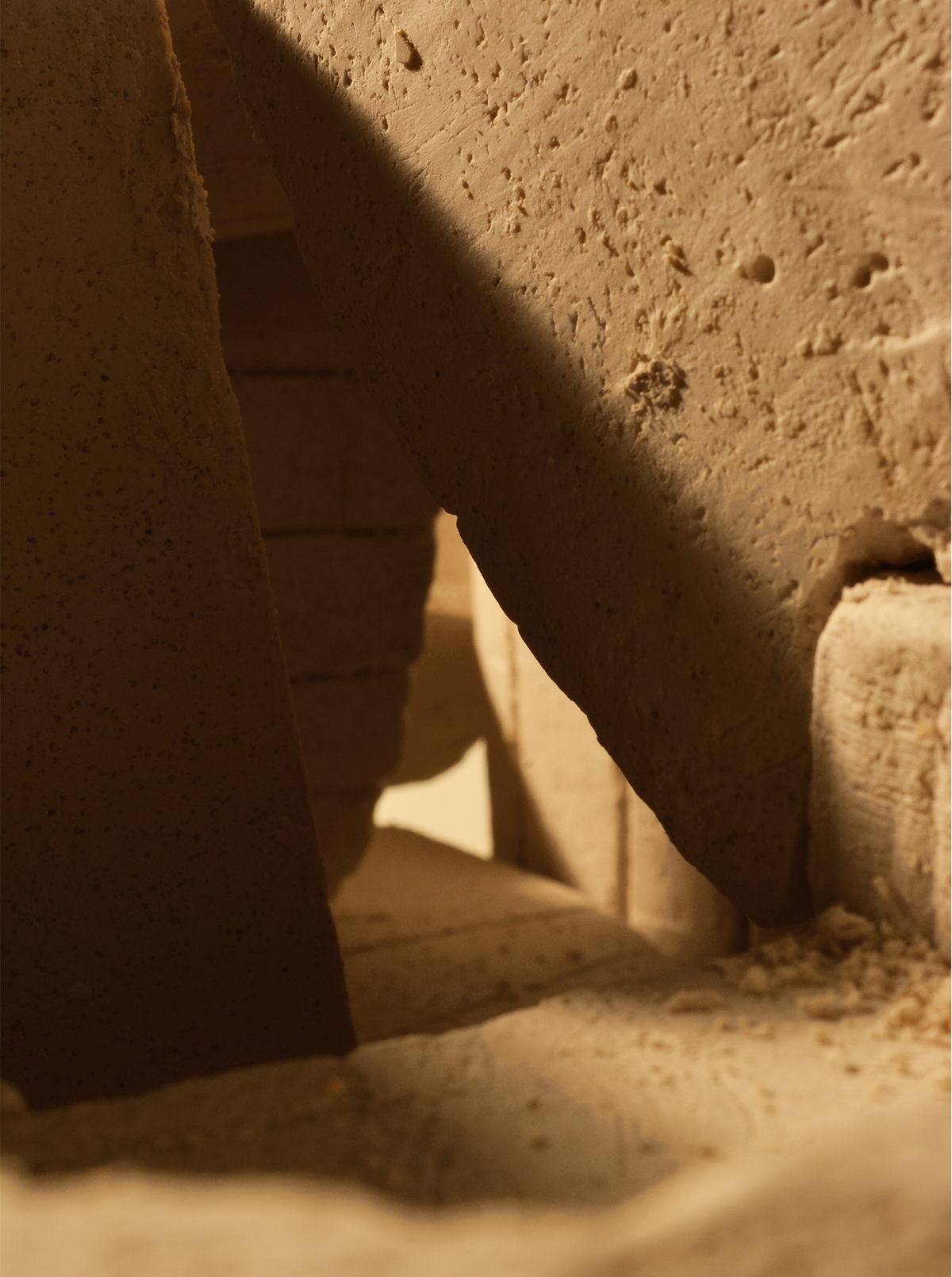
From that proposed excavation technique, it has been developed a building principle and an architectonic language and set of compositive rules that can hold the tension between the quarried place and the blocks extracted. The resultant architecture grows from the void in the excavation and creates an ambiguous continuity of formal and material language, of sizes and traces that change its position but constantly refer ones to the others, moving from the tectonics of the void to the stereotomy of the developed stone blocks assemblage.
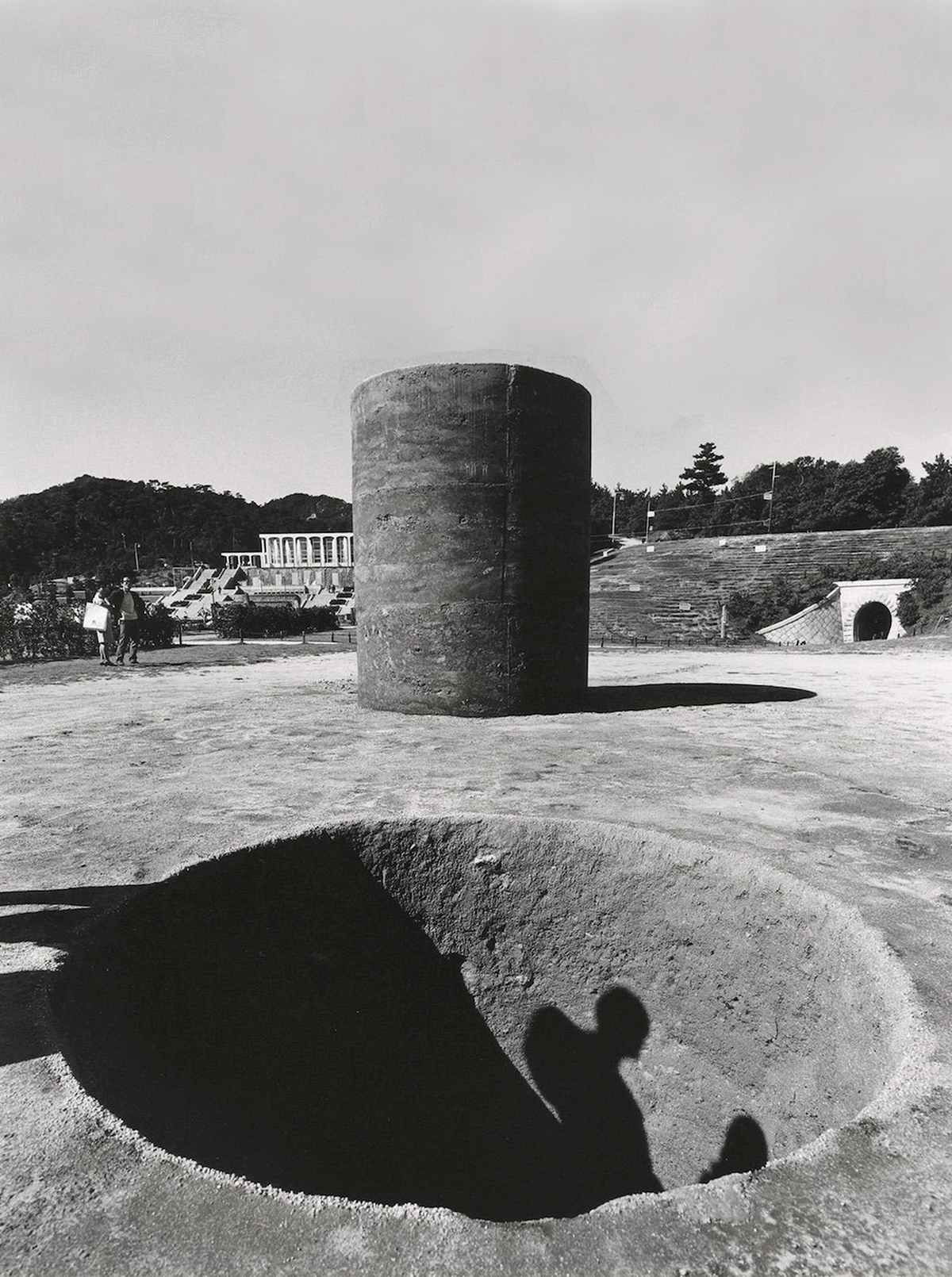
As we can learn from japanese sculpture master Nobuo Sekine, in his sculpture Phase-Mother Earth from 1968; It is trough constructed and specific form, readability of actions happened during the process of making, and material traces and density, that we can keep alive the dialogue and tension between a piece of matter and its void, the left space where is coming from. This lesson has been the starting point of the research here exhibited.
Ways of making. Material research
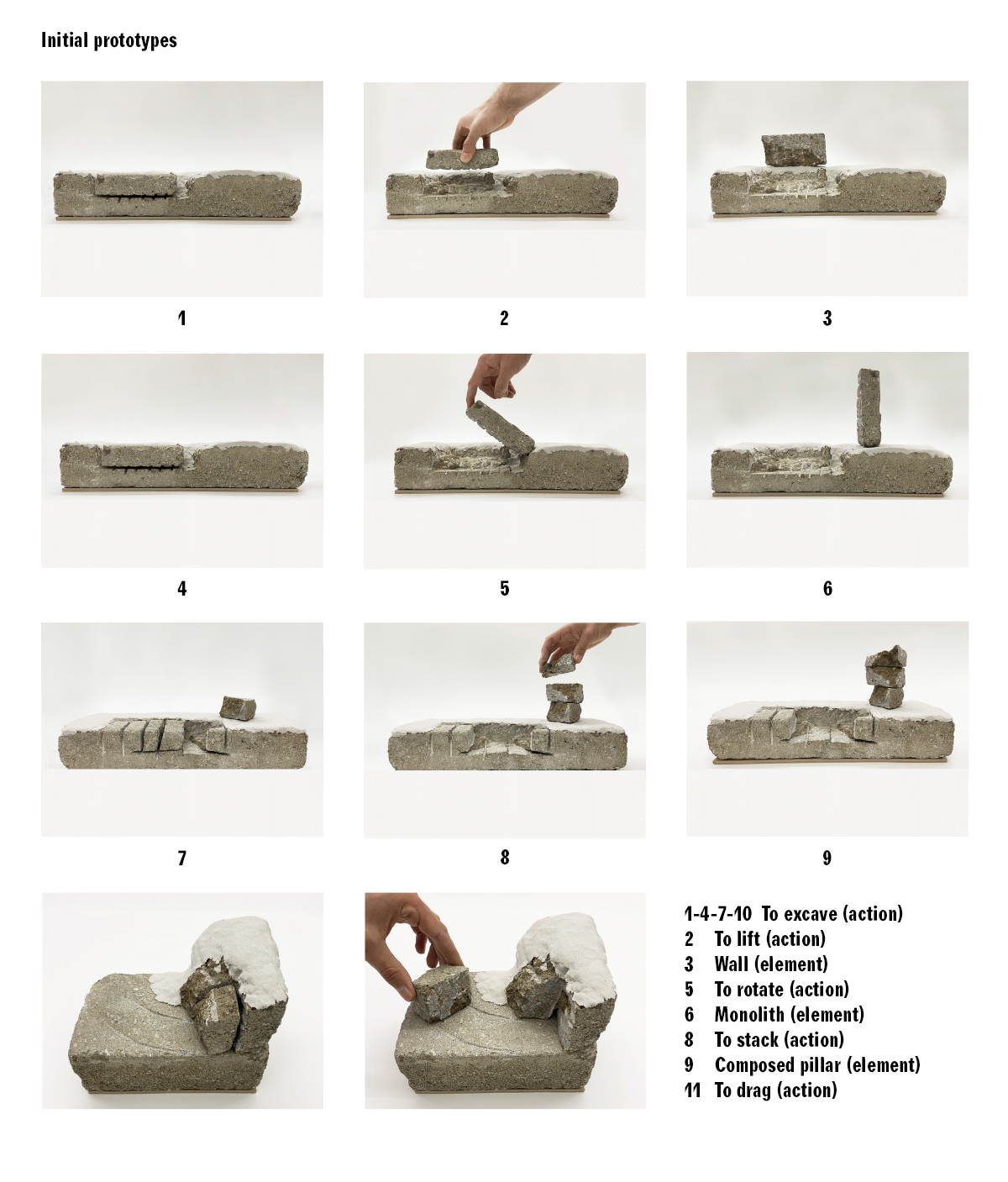
In the initial prototypes, the first approach to the project has been to explore the actions involved in the process of quarrying (to excavate, to move away and to place the material quarried); actions that are the basic tools to start creating relations of tension and dialogue between the left void and the resultant piece of stone.
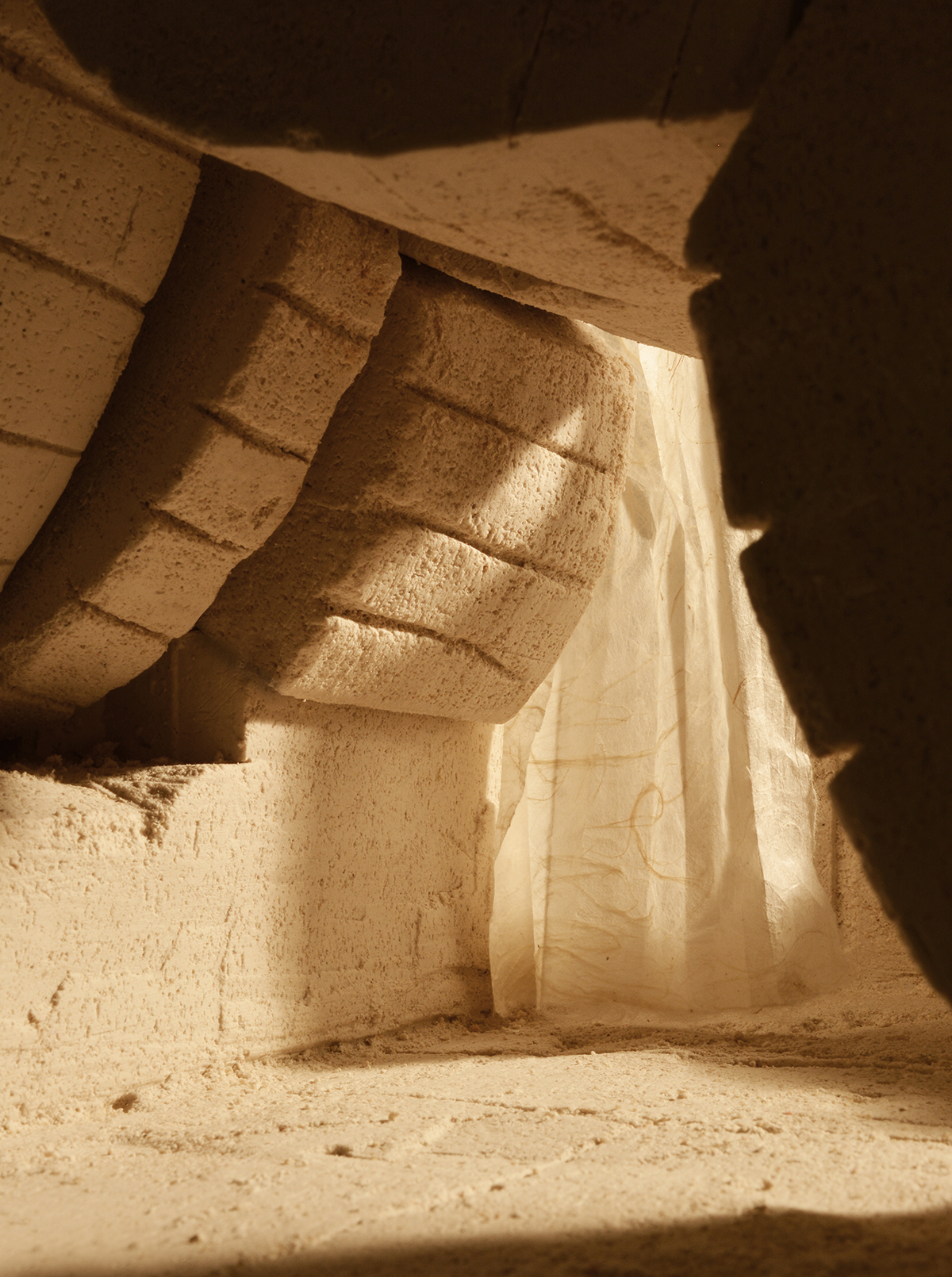
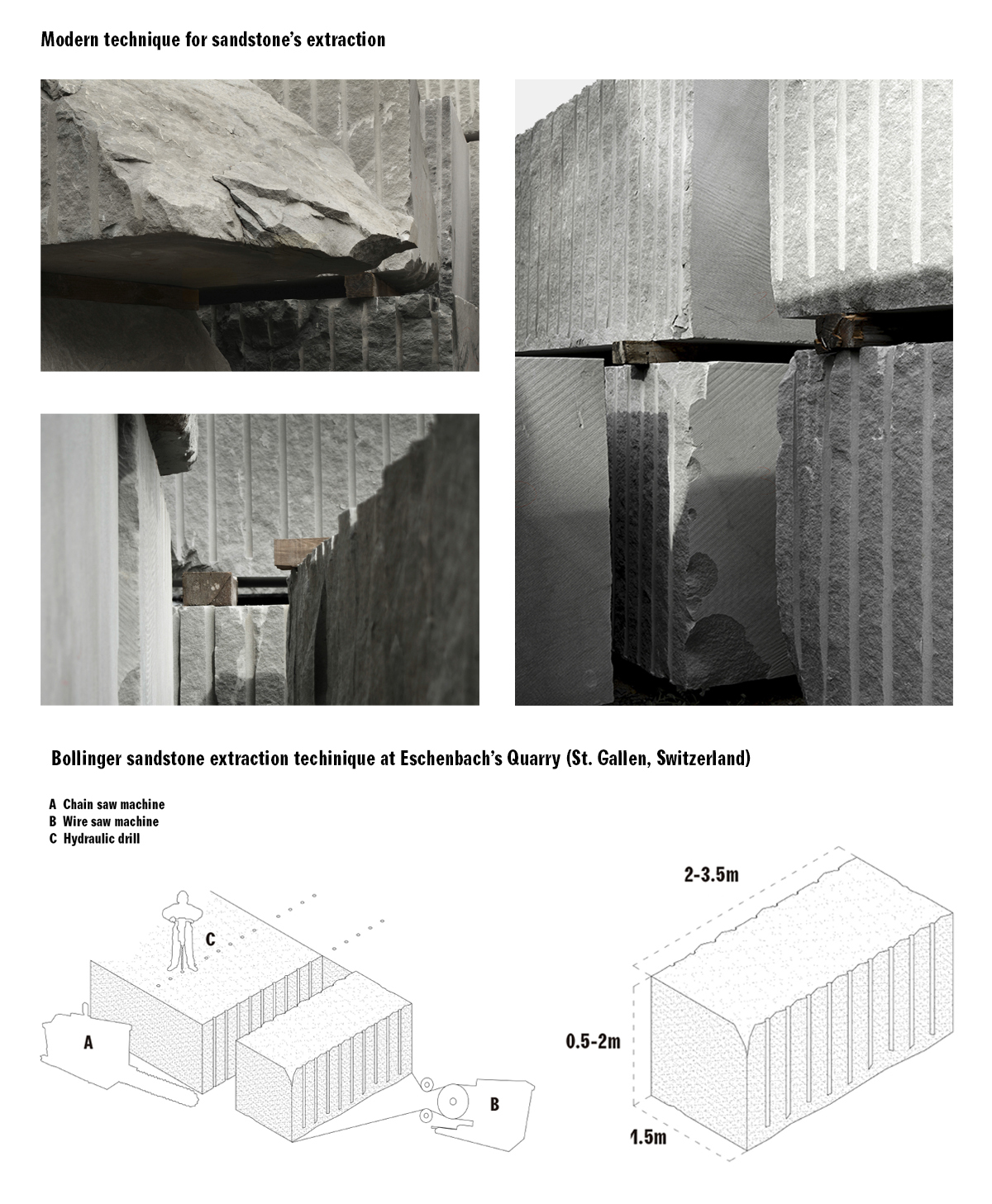
During the extraction technique’s development, it is proposed to take advantage from the diversity of tools and dimensions present the Eschenbach’s technique for extracting Bollinger sandstone, introducing with the hydraulic driller a curve in the block of Marès; a specific and strong form that can be easy identifiable after the process of extraction and so hold the tension between void and matter.
First attempts to generate architectonic spaces implementing the developed technique in a more complex quarrying strategy point out an essential characteristic: When the quarried blocks aren’t modified, the deeper we quarry, the thicker the pieces are. This creates a dependent relation between the depth of the space and the architectonic elements the blocks can perform.
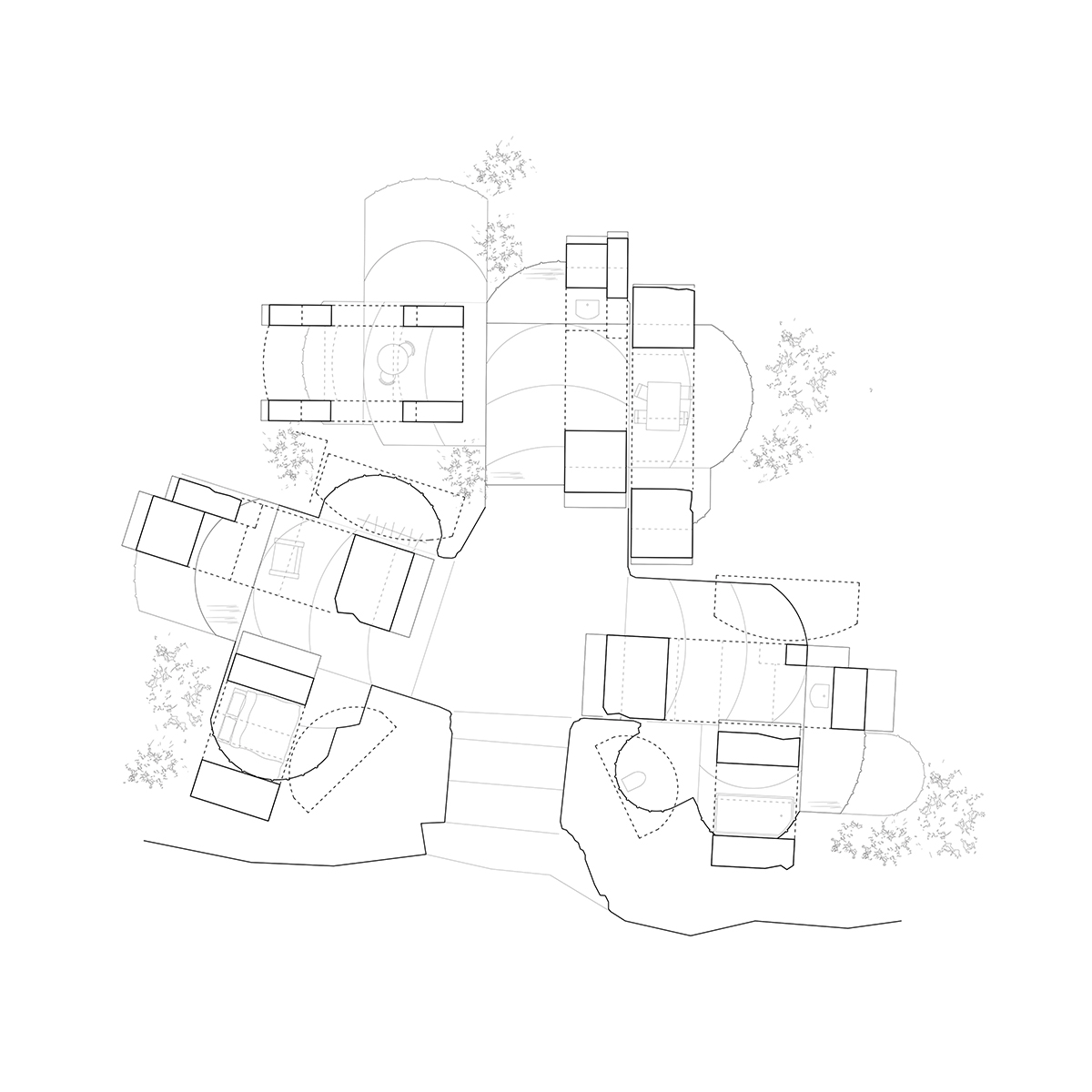
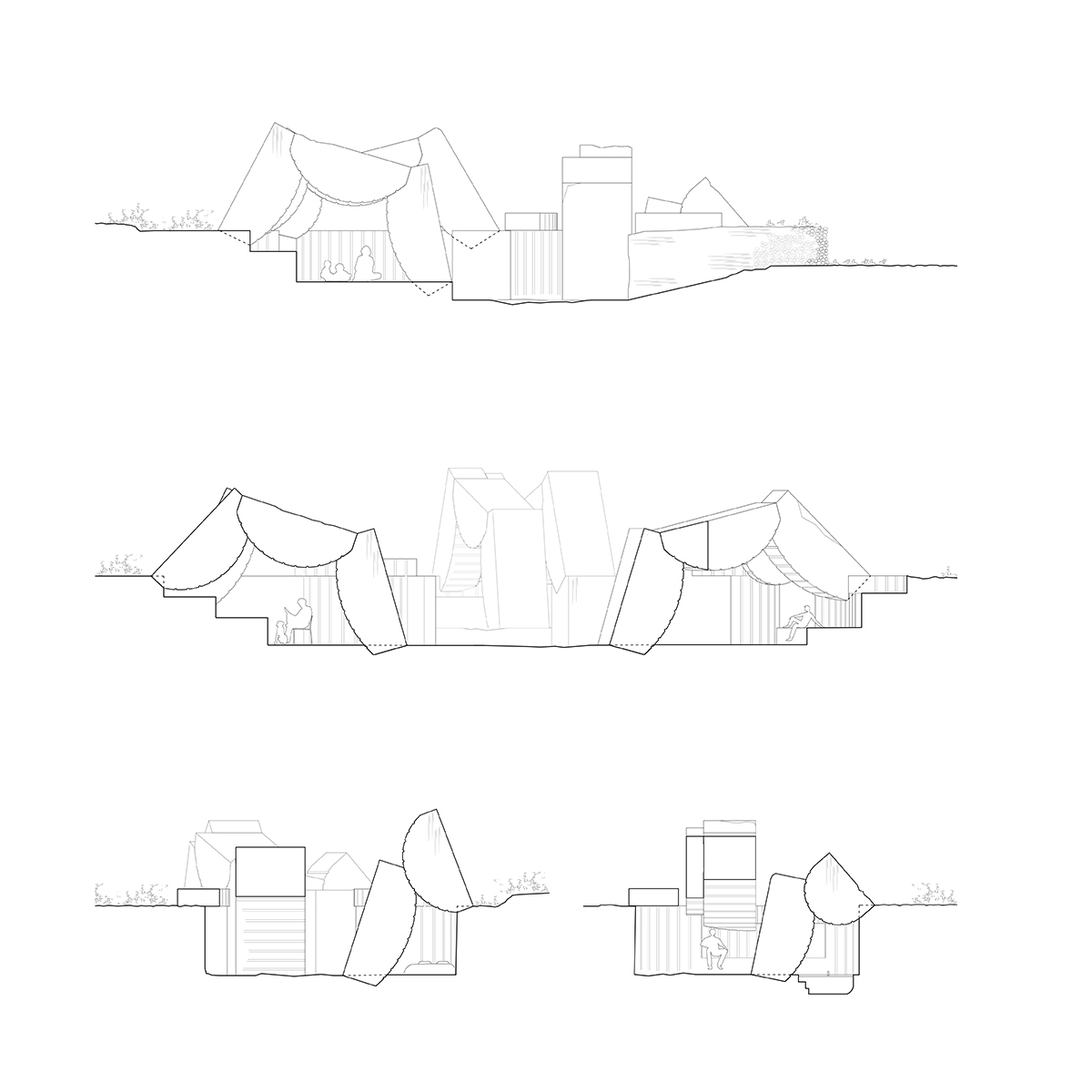
To excavate is/as to build. Final proposal
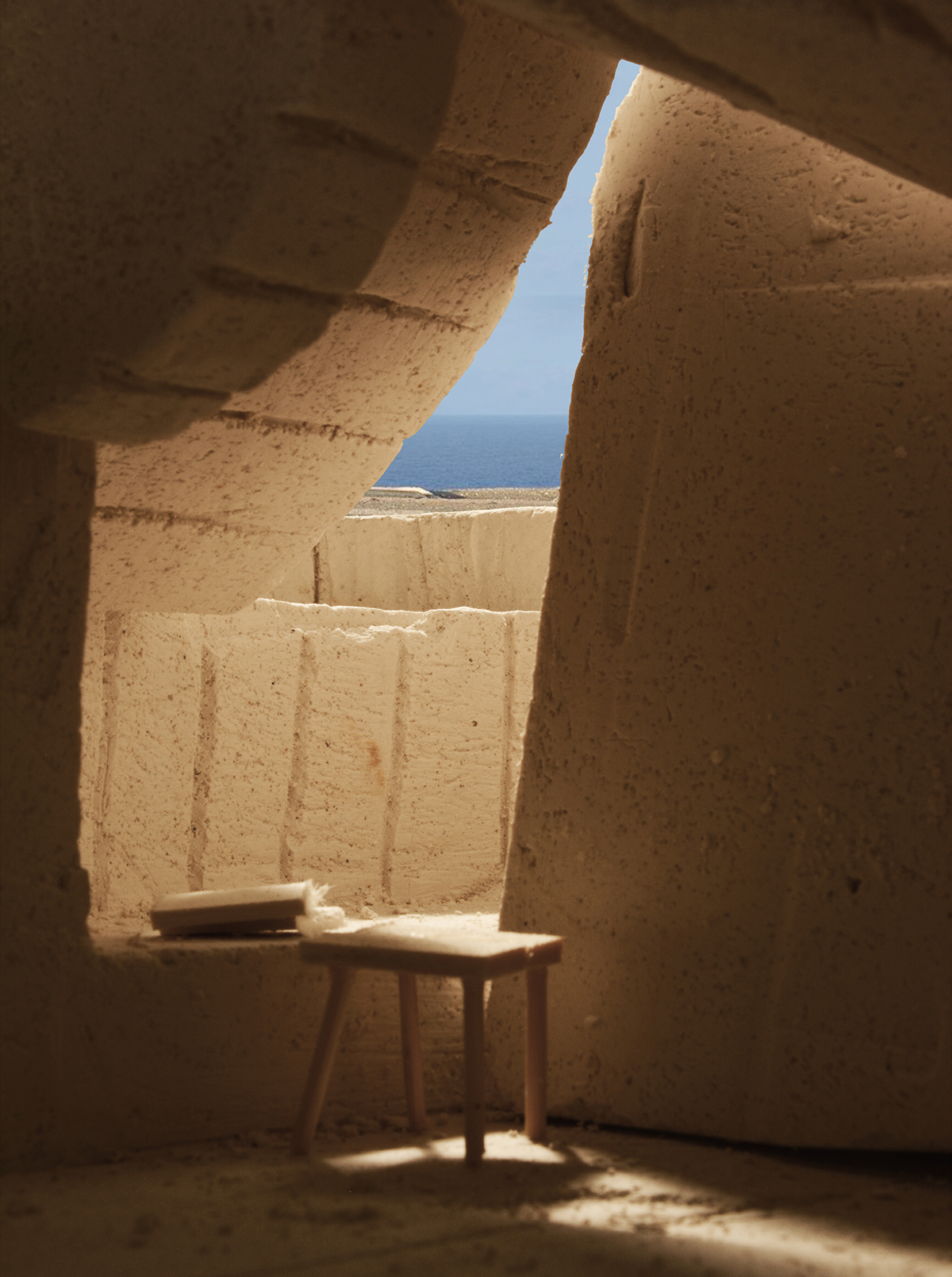
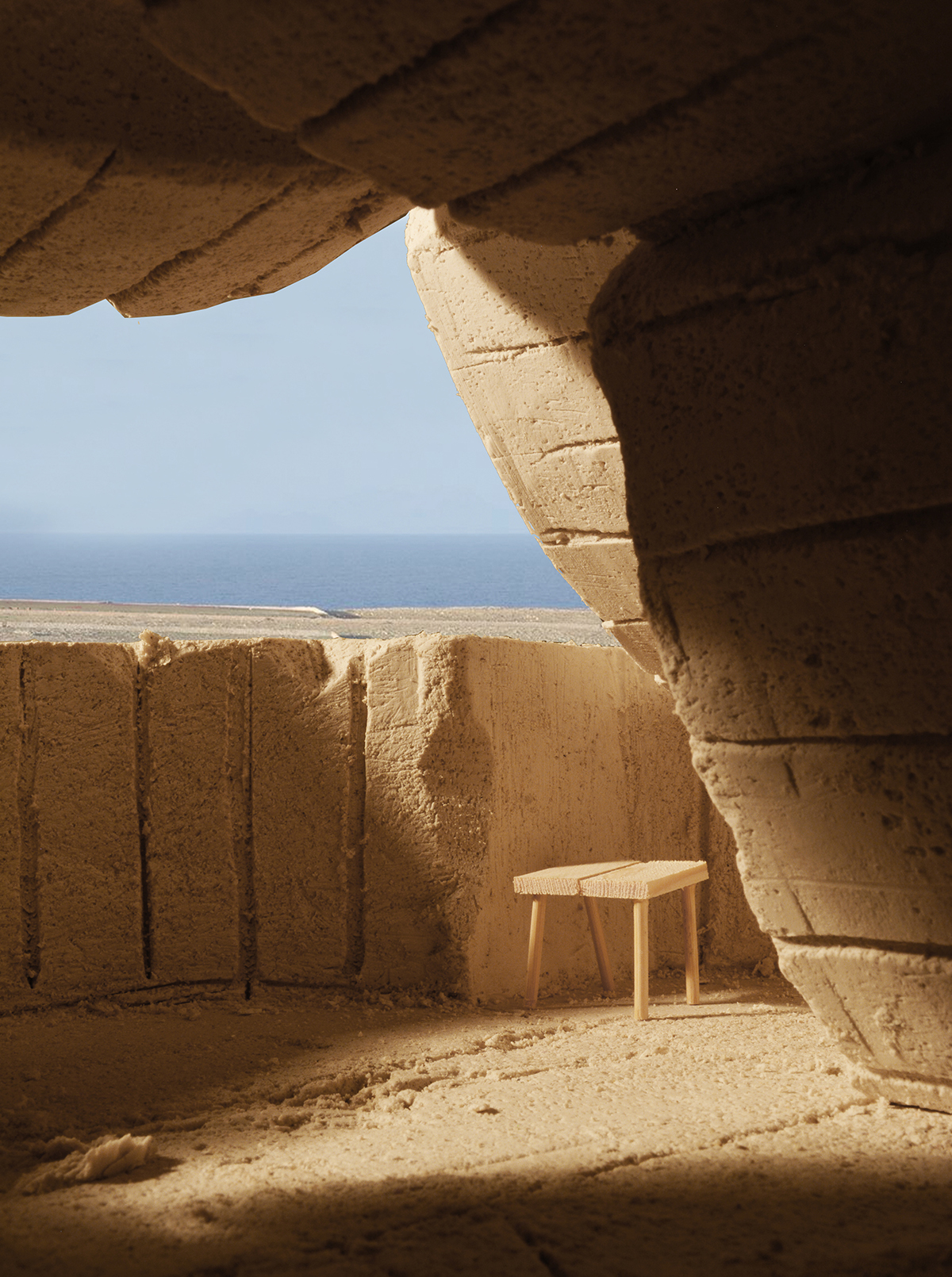
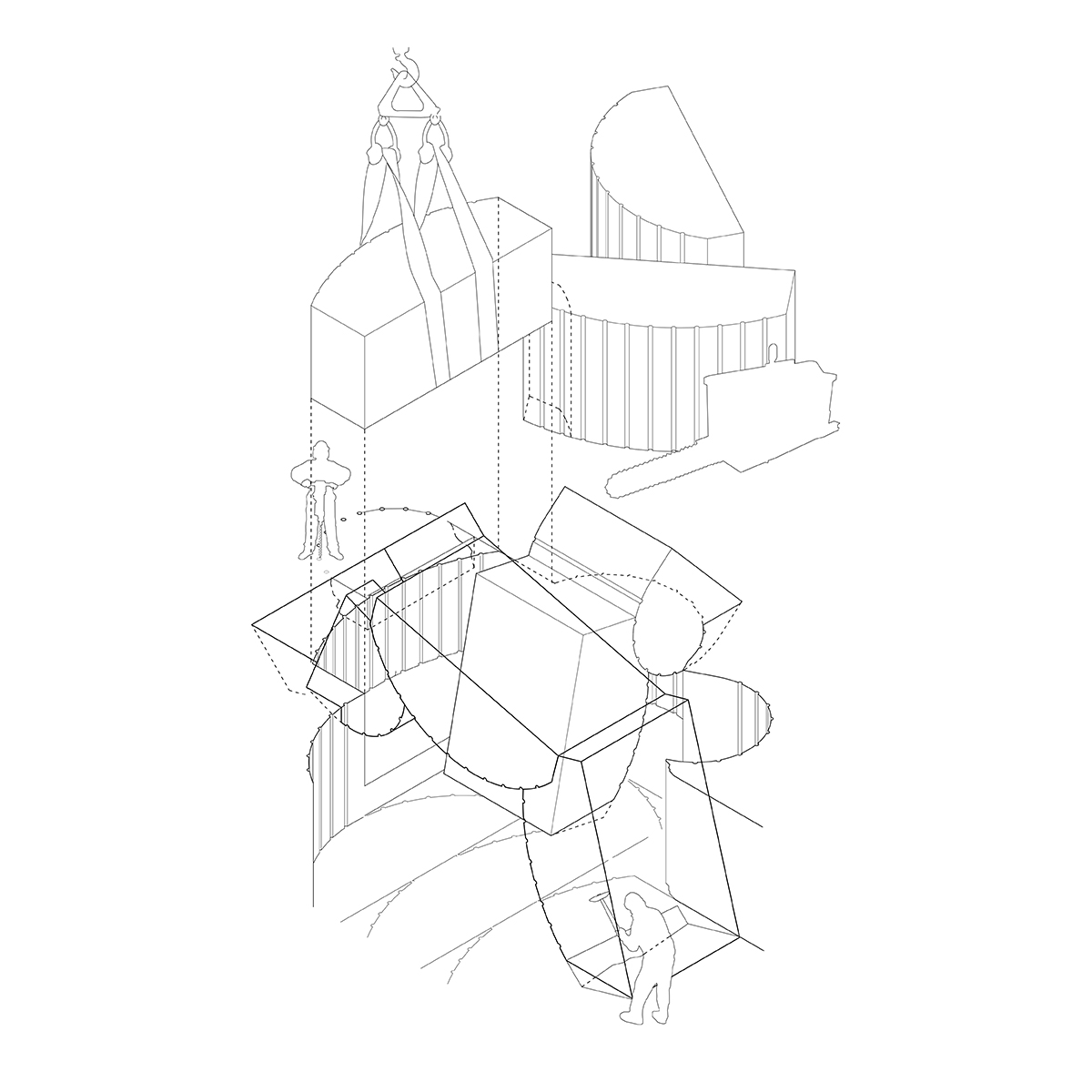
We enter to the final proposal by the definition of a building principle. It comes from the extraction, but also allows us to create spaces-in-between the tectonics of void and the stereotomy of construction. The assemblage system adds a new layer of complexity to the resultant architecture where the continuity of the formal language becomes more ambiguous.
This building principle brings us to a process of extraction and construction where, through a set of compositional rules and constructive needs, all the quarried pieces end up finding its place on the new space. The dialogue generated by the technique in form and traces now is hold by the spatial design between the whole quarried space and the built architecture.
The plans and sections of the complete architectural proposal come from the application and repetition of this defined process and its constructive rules.
Esta entrada aparece primero en HIC Arquitectura http://hicarquitectura.com/2022/01/roman-fernandez-vila-to-excavate-is-as-to-build/










No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario